Nous vous livrons ici deux études publiées par le Parlement européen dont les contenus sont intéressants pour l'approche capacitaire de la défense ainsi que pour les éléments liés à la préférence européenne industrielle notamment de défense (pochain événement Buy Euorpean Act)
Here you will find two studies published by the European Parliament whose contents are interesting for the defense capability approach as well as for elements related to the European industrial preference, especially defense (next event about Buy European Act)
European armaments standardisation
31-10-2018
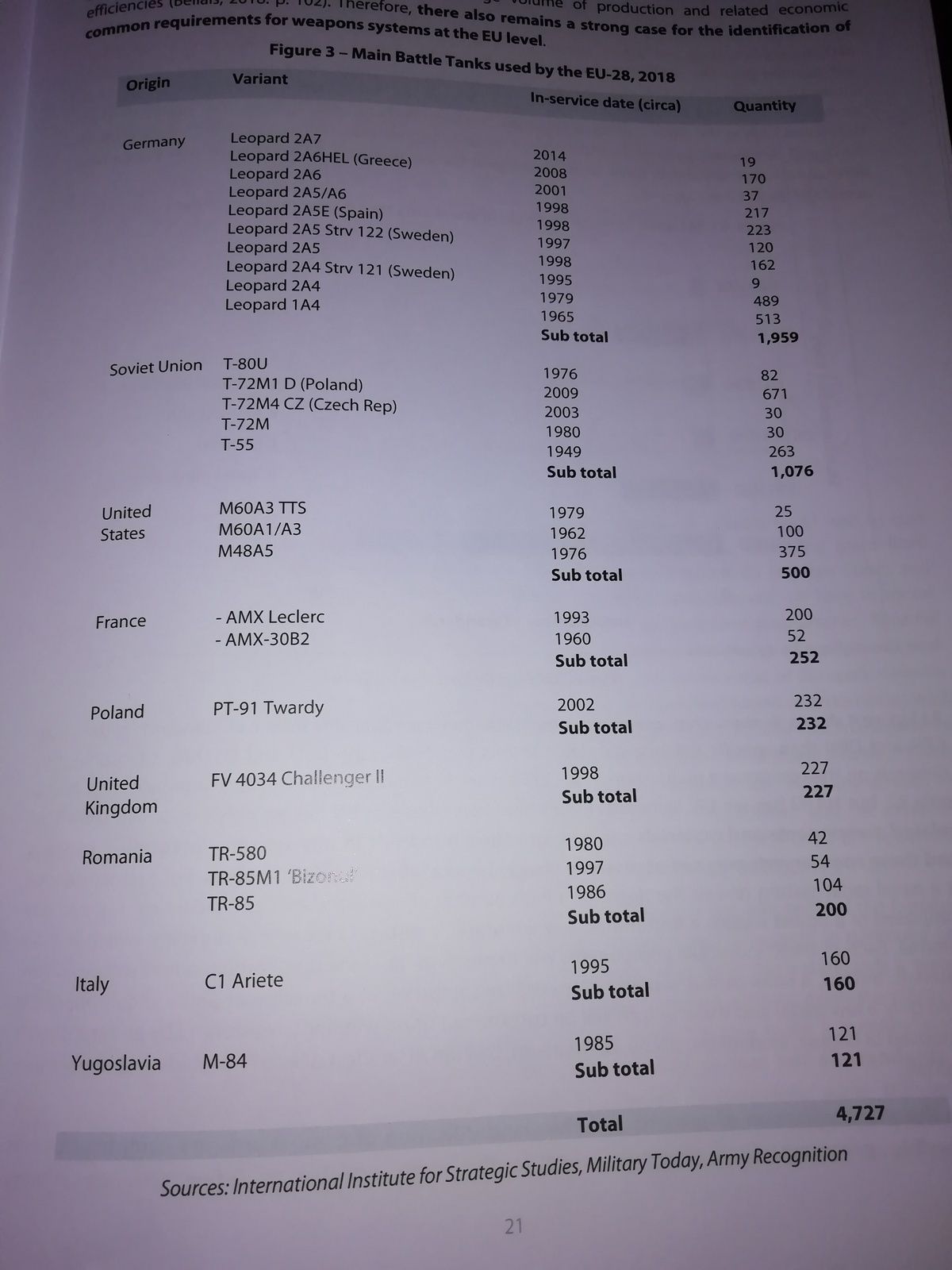
The standardisation of armaments has been a long-standing focus of EU efforts to enhance the Union’s military effectiveness, to improve capability development and to support the competitiveness of the European defence industry. Armaments standardisation is a process that can lead to cost savings for defence spending by injecting added-value in defence production processes and the avoidance of capability and equipment duplication. Standardisation is a method of improving interoperability within and between European armed forces and a process that can enhance the operational effectiveness of Europe’s militaries. Both the EU and NATO have taken measures over many years and decades to enhance armaments standardisation in Europe. Yet the nature of the contemporary global defence market is that many more technologies and components integrated into military systems are sourced and/or produced in the civilian sector. The line drawn between defence equipment and capabilities on the one hand, and civilian products and technologies on the other, is increasingly blurred. In this context, and in relation to recent developments on EU defence cooperation, this study analyses the standardisation approaches taken by the EU in relation to maritime information sharing and remotely piloted aircraft systems. It makes recommendations on how EU approaches to armaments standardisation can be expanded and enhanced.
The Extra-EU Defence Exports’ Effects on European Armaments Cooperation
20-04-2015
Are exports made to countries outside of the European Union (EU) impeding European cooperation in armaments? Although the numbers vary significantly from one country to another, the European Defence Technological and Industrial Base (EDTIB) now collectively derives an important share of its collective turnover from extra-EU export sales. Accordingly, EU Member states devote important political, financial and administrative resources to support and promote their national producers in major competition overseas. The current scarcity of common European programmes, and the limited impacts of recently introduced legislation designed to harmonize national defence procurement rules and to facilitate intra-EU transfers, could indicate that extra-EU exports are detrimental to European cooperation on weapons projects. This negative effect would primarily come from introducing greater levels of competition between European companies creating greater tensions, which are not conducive to cooperation on the EU level. The study finds that there is indeed a correlation between competition for major foreign markets and difficulties of intra-EU cooperation but makes the analysis that extra-EU exports are more a symptom of structural constraints faced by major suppliers, such as the weakness of defence spending in European countries, and the persistence of fragmentation and duplication of production capabilities.

/image%2F0122211%2F20230208%2Fob_158fc6_ob-dd851d-logo-irce-hd.jpg)